-
In 5G dual connectivity, On what basis is the master and secondary node decided?
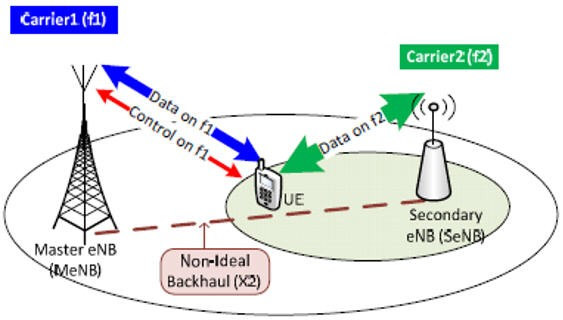
In 5G dual connectivity, the determination of the master and secondary nodes is primarily based on the hierarchical relationship between the two nodes and their roles in providing connectivity to the User Equipment (UE). The master and secondary roles are typically assigned as follows: The decision of which node serves as the master and which…
-
What is difference between carrier aggregation and dual connectivity in 5G?
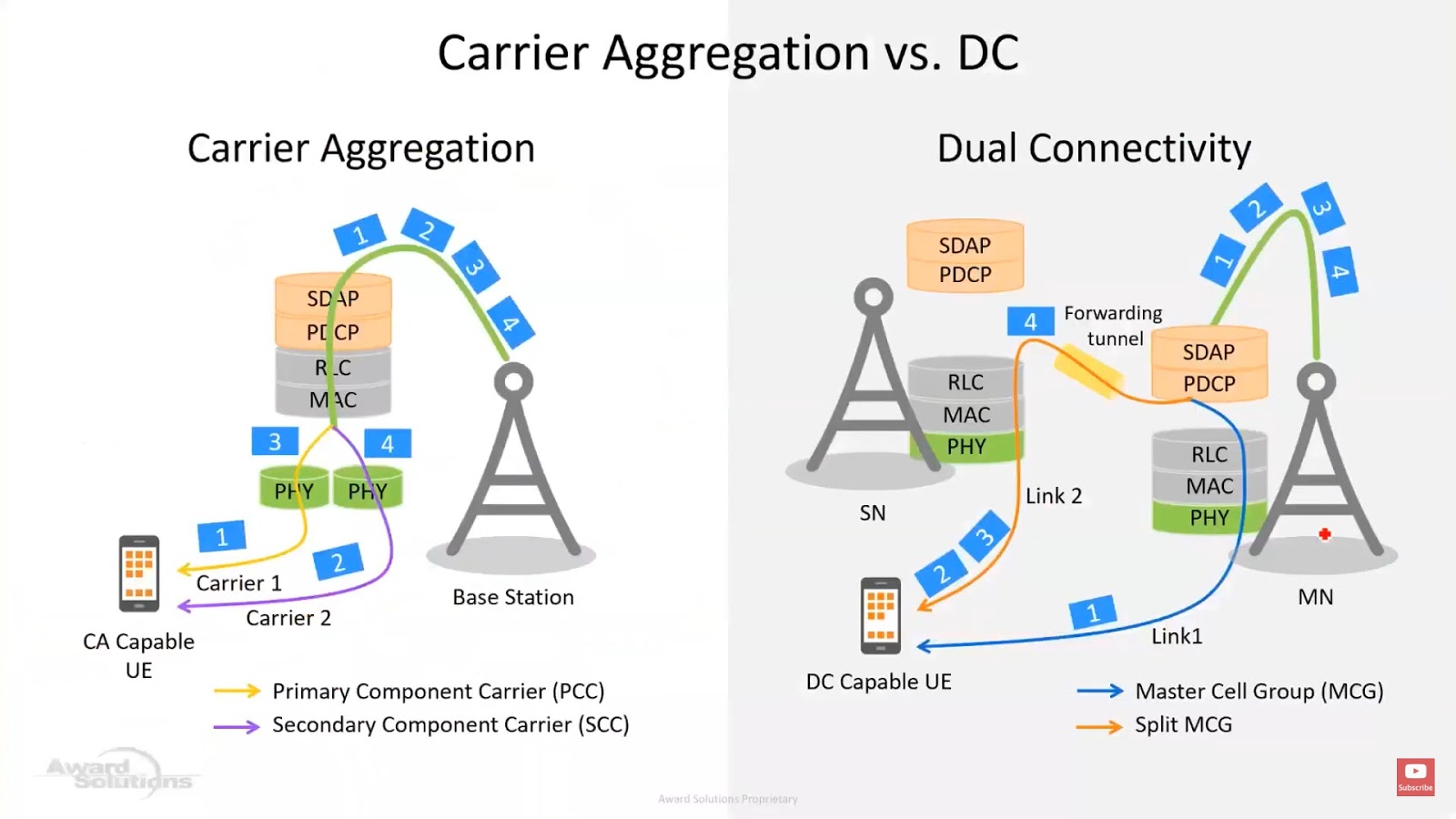
Carrier Aggregation and Dual Connectivity are both techniques used in 5G to enhance data speeds and increase network capacity. However, they are distinct technologies with different purposes and implementations: Carrier Aggregation: Carrier Aggregation (CA) is a technique used in 5G (and also in LTE-Advanced) that allows mobile devices to simultaneously use multiple frequency bands from…
-
SECURITY EDGE PROTECTION PROXY (SEPP)
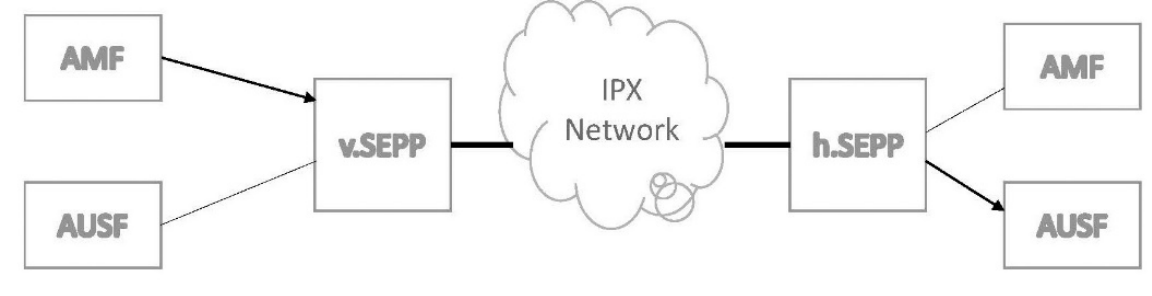
To protect messages that are sent over the N32 interface, the 5G system architecture implements Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) at the perimeter of the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) network. SEPP receives all service layer messages from the Network Function (NF) and protects them before sending them out of the network on the N32…
-
ANTENNA ARRAY STRUCTURE FOR ONE AND TWO-DIMENSIONAL BEAMFORMING
The purpose of using an antenna array, as shown in Figure 7.1-A, is to enable high gain beams and the ability to steer those beams over a range of angles. The gain is achieved, in both UL and DL, by constructively combining signals from a number of antenna elements. The more antenna elements utilized, the…
-
4G -5G INTERWORKING ARCHITECTURE:
Through our work with several mobile providers, we learned that majority of 5G deployments will be brownfield with upgrade from existing 3G/4G network. For mobile providers deploying 5G as greenfield new network, it has to interwork with 4G for roaming with other providers in same country or international roaming. Figure 1 provides a high-level overview…
-
Network Slicing in 5G
A network slice is a logical network serving a defined business purpose or customer, consisting of all required network resources configured together. It is created, changed and removed by management functions. Hence network slicing divides an operator’s physical network into multiple logical networks. These logical networks would permit the implementation of tailor-made functionality and network…
-
5G Vs WiFi – Convergence or Competition
Guest post by Dr. Rizwan Ghaffar (linkedin) With the 5G deployment spreading rapidly, there is a question of what would be the future of Wi-Fi in the world connected by 5G. In my opinion, Wi-Fi and WWAN (wireless wide area networks) will continue their convergence/competitive journey along the road. They will coexist and play an…
-
Question: From the perspective of UE why 5G is more secure than 2G/3G/4G?
Answer: The 2G GSM systems were the first digital systems that performed the authentication of subscriber. The mobile was assigned a temporary identifier after the authentication so that it does not has to send the mobile subscriber’s permanent identity ‘IMSI’ on the air interface. And the voice was encrypted. However, 2G systems suffered from two…
-
7. IMS Procedure: VoLTE Call
The initial stages of setting up a VoLTE call are the processes of the initial attach, P-CSCF discovery and creating the default bearer for SIP signaling (by registering with the IMS network and subscribing to a registration eventpackage).The first step in a VoLTE call setup is a SIP INVITE request initiated by the calling UE.…
-
Voice and Video services over IMS in 5G
5G voice/video service will still be provided based on IMS (5G as one of the access modes for IMS voice/video), and the introduction of 5G voice/video will not change the IMS network architecture. Support of IMS based services is based on GSMA NG.114 “IMS Profile for Voice, Video & Messaging over 5GS”. In the early…