-
In 5G dual connectivity, On what basis is the master and secondary node decided?
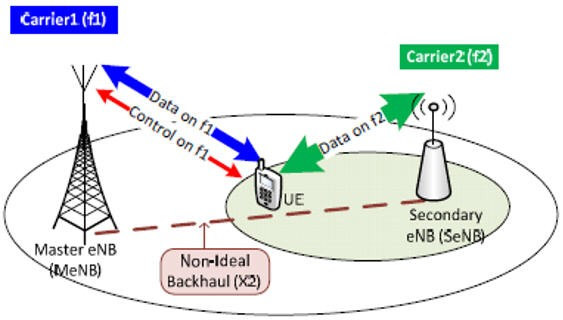
In 5G dual connectivity, the determination of the master and secondary nodes is primarily based on the hierarchical relationship between the two nodes and their roles in providing connectivity to the User Equipment (UE). The master and secondary roles are typically assigned as follows: The decision of which node serves as the master and which…
-
What is difference between carrier aggregation and dual connectivity in 5G?
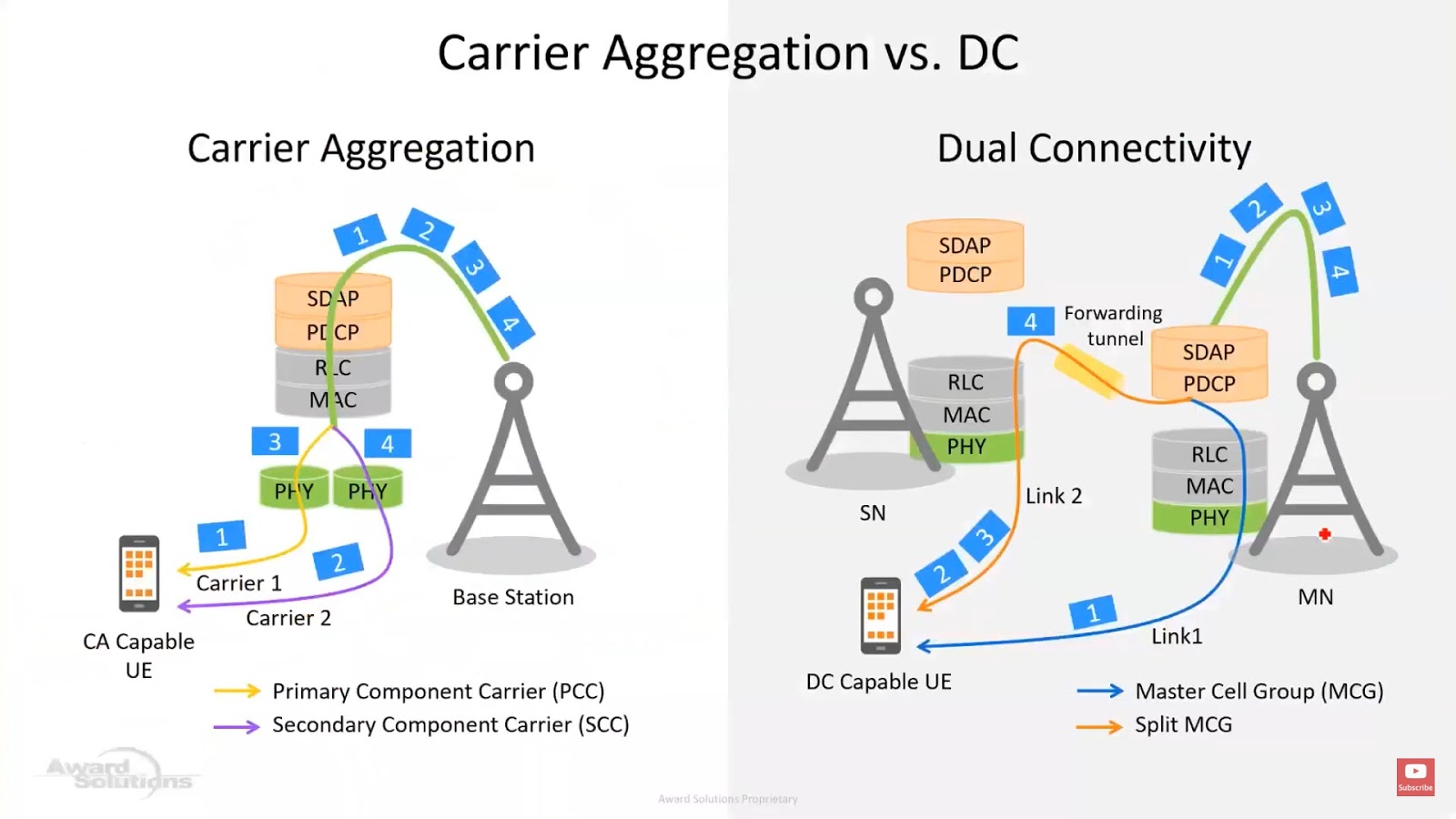
Carrier Aggregation and Dual Connectivity are both techniques used in 5G to enhance data speeds and increase network capacity. However, they are distinct technologies with different purposes and implementations: Carrier Aggregation: Carrier Aggregation (CA) is a technique used in 5G (and also in LTE-Advanced) that allows mobile devices to simultaneously use multiple frequency bands from…
-
What is difference between Access Stratum (AS) and Non-Access Stratum Signalling in 5G?
In 4G & 5G, the signalling between UE and mobile network can be divided into two types: the Access Stratum (AS) and the Non-Access Stratum (NAS), each responsible for different functions: In summary, the Access Stratum (AS) in 5G focuses on radio-related functions and signaling, dealing with the communication between the UE and the radio…
-
4G LTE Interview Questions 1
Q. What is Difference between MIB and SIB? MIB and SIB are two types of System Information (SI) that is broadcasted in the serving are of particular cell. SI is carried by the logical channel BCCH, which in turn is carried by either of the transport channels BCH or DL-SCH.Master information Block (MIB): is a…
-
2G GSM Interview Questions & Answers

Q1) How we can use the same frequency like (F1) in two neighbor cell (site) in the same cluster but do not have interference?? Answer) We can do this by we reduce the power of the frequency (F1) in two sites than other frequencies, this mean that the coverage area of frequency (F1) have small…
-
Question: Is there Tracking Area Update (TAU) procedure in 5G like we see in 2G, 3G and 4G?
Answer: In 5G we have Registration Area Update (RAU) instead of Tracking area Update (TAU). A Registration area is a list of tracking areas that are assigned to UE by 5G Network. This is especially useful in the high mobility scenarios where assigning a tracking area list (Registration Area) to UE reduces the signalling on…
-
SECURITY EDGE PROTECTION PROXY (SEPP)
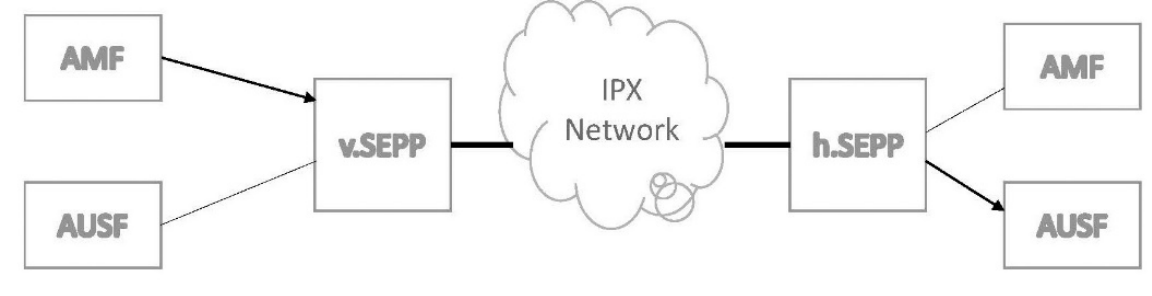
To protect messages that are sent over the N32 interface, the 5G system architecture implements Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) at the perimeter of the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) network. SEPP receives all service layer messages from the Network Function (NF) and protects them before sending them out of the network on the N32…
-
3GPP 5G SECURITY ARCHITECTURE
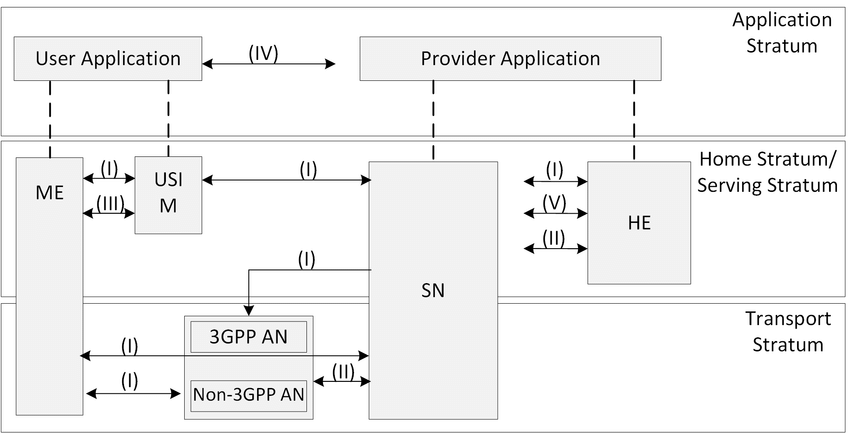
3GPP defines the overall 5G security architecture, illustrated in Figure above. This includes many network architectural elements and concepts such as: Network access security (I) which is the set of security features that enables user equipment (UE) to authenticate and access services via the network securely, including 3GPP access and non3GPP access, and particularly to…
-
What is the difference between CU and DU in 5G?
In 5G the basestation is called as the gNB. According to the 3GPP recommendation TR 38.801, the gNB is further subdivided into the Centralized Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU) as shown in the diagram below. The Centralized Unit is used to support higher layer protocols like SDAP, PDCP, and RCC. While the lower layer…
-
Enhanced Common Public Radio Interface (eCPRI)
Background Although Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) has been the main Fronthaul interface standard, many operators started to question its suitability to high bandwidth 5G use cases. Improvements to efficiency and link capacity utilization were requested. Also advanced networking and OAM features of mainstream packet transport standards were requested. What is CPRI? A digital public…