-
In 5G dual connectivity, On what basis is the master and secondary node decided?
In 5G dual connectivity, the determination of the master and secondary nodes is primarily based on the hierarchical relationship between the two nodes and their roles in providing connectivity to the User Equipment (UE). The master and secondary roles are typically assigned as follows: The decision of which node serves as the master and which…
-
ANTENNA ARRAY STRUCTURE FOR ONE AND TWO-DIMENSIONAL BEAMFORMING
The purpose of using an antenna array, as shown in Figure 7.1-A, is to enable high gain beams and the ability to steer those beams over a range of angles. The gain is achieved, in both UL and DL, by constructively combining signals from a number of antenna elements. The more antenna elements utilized, the…
-
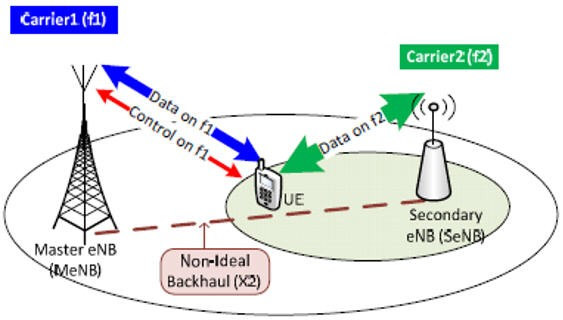
4G -5G INTERWORKING ARCHITECTURE:
Through our work with several mobile providers, we learned that majority of 5G deployments will be brownfield with upgrade from existing 3G/4G network. For mobile providers deploying 5G as greenfield new network, it has to interwork with 4G for roaming with other providers in same country or international roaming. Figure 1 provides a high-level overview…
-
Network Slicing in 5G
A network slice is a logical network serving a defined business purpose or customer, consisting of all required network resources configured together. It is created, changed and removed by management functions. Hence network slicing divides an operator’s physical network into multiple logical networks. These logical networks would permit the implementation of tailor-made functionality and network…
-
Q: Why in 5G, in addition to IP PDU session type, Ethernet PDU session type was introduced?
Answer: In the IP PDU session type, the IP packets have source and destinations IP addresses in the IP header (e.g., an ipv6 adress is 128bits). As a result, this increases the size of the IP packet header. This is quite inefficient in mMTC and uRLLC use cases of 5G. In the scenario of mMTC,…