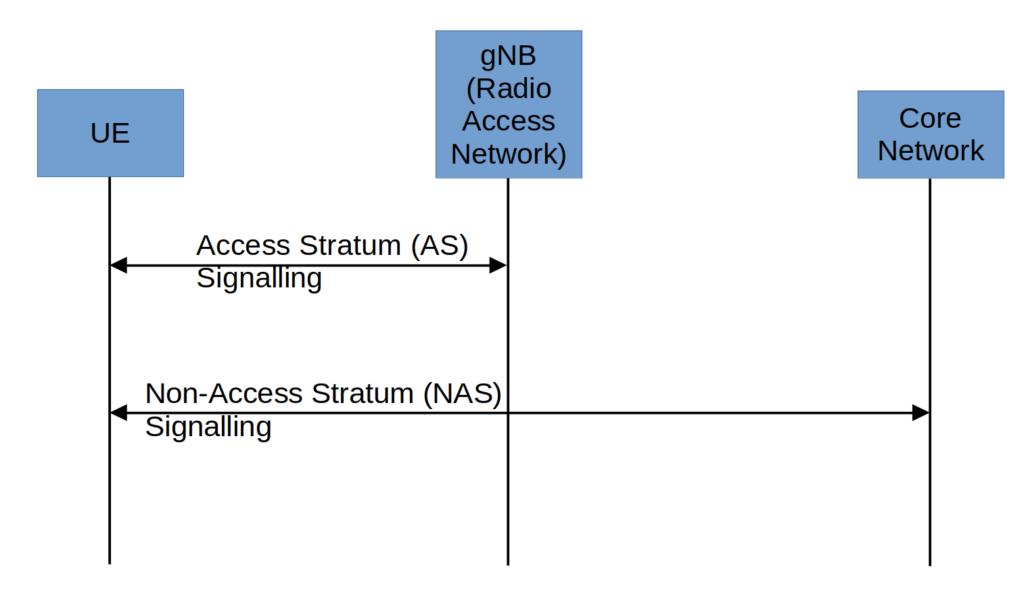
In 4G & 5G, the signalling between UE and mobile network can be divided into two types: the Access Stratum (AS) and the Non-Access Stratum (NAS), each responsible for different functions:
- Access Stratum (AS) signalling handles the radio interface and communication between the user equipment (UE) and the radio access network (RAN). It deals with the establishment, maintenance, and termination of radio bearers, which are the logical channels used to transmit user data and control information over the air interface. The main functions of the Access Stratum include:
- Radio Resource Control (RRC): RRC manages the connection setup and configuration between the UE and the RAN. It controls the radio resources and manages mobility-related procedures, such as handovers between cells.
- Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP): PDCP is responsible for header compression and decompression, as well as ciphering and deciphering the user data packets.
- Radio Link Control (RLC): RLC ensures the reliable transmission of user data over the air interface by providing error correction, segmentation, and reassembly of data packets.
- Medium Access Control (MAC): MAC handles the scheduling and prioritization of data transmission between multiple UEs and the RAN.
- Non-Access Stratum (NAS) signalling the handles the signaling and communication between the UE and the core network (CN). It is responsible for controlling the mobility and session management of the UE. The main functions of the Non-Access Stratum include:
- Session Management (SM): SM handles the establishment, modification, and termination of communication sessions between the UE and the core network. It manages the bearer services and mobility procedures between different access networks.
- Mobility Management (MM): MM is responsible for tracking the UE’s location, managing location updates, and handling authentication and security-related procedures during the mobility of the UE.
- Connection Management (CM): CM manages the establishment, modification, and termination of connections between the UE and the core network.
In summary, the Access Stratum (AS) in 5G focuses on radio-related functions and signaling, dealing with the communication between the UE and the radio access network (RAN). On the other hand, the Non-Access Stratum (NAS) handles core network-related functions and signaling, managing the communication between the UE and the core network (CN). This separation of functions allows for better scalability, flexibility, and efficiency in 5G networks.