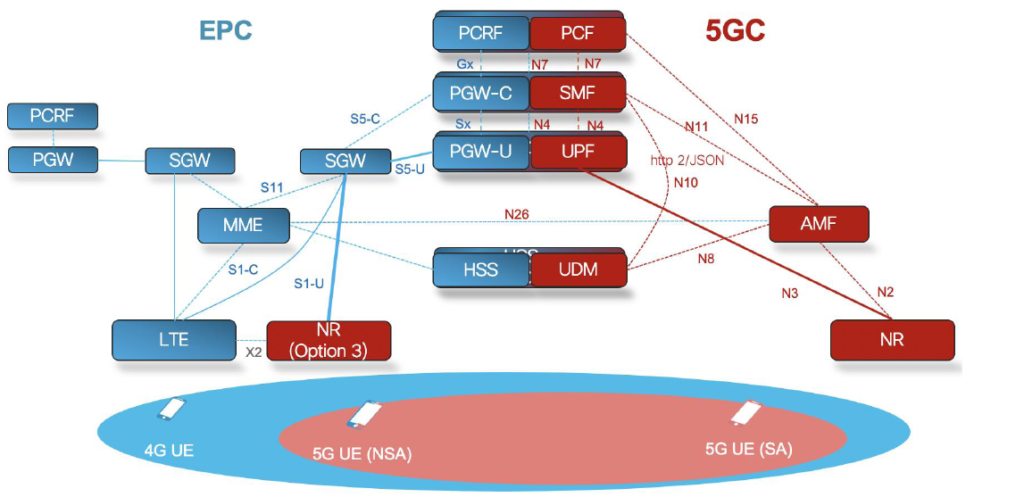
Through our work with several mobile providers, we learned that majority of 5G deployments will be brownfield with upgrade from existing 3G/4G network. For mobile providers deploying 5G as greenfield new network, it has to interwork with 4G for roaming with other providers in same country or international roaming. Figure 1 provides a high-level overview of 4G and 5G network. For clarity all 4G network functions (NF) are on left side (in blue) and 5G network functions are on right side (in red).
5G network description can be overwhelming and confusing therefore we have depicted very simplified version of interworking architecture with explanation from top-down. Technical readers can go through 5G system architecture for more details.
- 5G technology is not about higher bandwidth but capability with differentiated services and quality of experience (QoE). In 5G subscriber services are managed by policy control function (PCF) therefore we need seamless user experience by managing, notifying and ability to charge differently for 5G network usage.
- 5G system network architecture is divided into control and user plane separation because they can scale independently. 5G subscribers are terminated in session management function (SMF). SMF manage subscribers from the time the attach to network with power on to power-off or detach from network.
- 5G provider much higher bandwidth to subscribers along with low latency services support, therefore user plane function (UPF) are normally deployed at edge. You might hear about Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) or xEdge which normally contains UPF along with low latency applications deployed at edge. Since UPF handles large bandwidth and diverse set of users therefore bulk of traffic of offloaded at edge.
- When subscriber power-on their devices they go thru signaling phase they challenged and authenticated with proper credentials. In 4G entire signaling is handled by mobility management function 9MME) and in 5G this is handled by Access Management Function (AMF). In order to support interworking between 4G and 5G, we use interface which is referred as N26 [3].
- For 4G mobile, subscription information is stored in Home Subscriber System (HSS) whereas for 5G it is stored in universal data system (UDM). We need interworking between both HSS and UDM so that subscription related information is matched between 4G and 5G.
- The biggest change for any technology is at edge and 5G is no exception. New radio (NR) as name suggest provides capability and allow subscribers to use 5G network. We also have existing 3G and 4G radio at edge therefore we must have design considerations to avoid interference and handover mechanism so that user can avail any service available based on their device capabilities and subscription. 5G Non stand Alone (NSA) provide ability where 5G new radio sites can connect to existing 4G Core (4GC). 5G standalone (SA) provides capability where 5G new radio can connect only to 5G Core (5GC) as depicted above.
- When 4G was deployed, virtualization technology was not mature, so it was initially deployed on standalone physical devices and then transitioned into standardized ETSI Management and Orchestration (MANO) based virtualized network function (VNF) architecture on private/public cloud. 5G network functions are deployed as micro-services on cloud native, container-based clusters e.g. Kubernetes. To summarize, there is a difference between 4G and 5G network functions and the underlying cloud technologies. Also, the standards definition for 5G interworking with legacy 2G/3G technologies is in progress.